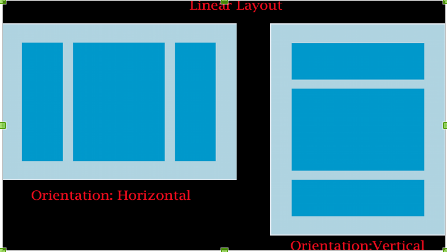
Linear Layout arranges other views either horizontally in a single column or vertically in a single row. It arranges its elements sequentially
Attributes
- android: orientation—Used for arranging the controls in the container in horizontal or vertical order
- android:layout_width—Used for defining the width of a control
- android:layout_height—Used for defining the height of a control
- android:padding—Used for increasing the whitespace between the boundaries of the control and its actual content
- android:layout_weight—Used for shrinking or expanding the size of the control to consume the extra space relative to the other controls in the container
- android:gravity—Used for aligning content within a control
- android:layout_gravity—Used for aligning the control within the container
Example
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:text="RED" android:id="@+id/TextView01" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#f00" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_weight=".14" android:gravity="center" android:textColor="#000"></TextView> <TextView android:text="ORANGE" android:id="@+id/TextView02" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_weight=".15" android:background="#ffa500" android:gravity="center" android:textColor="#000"></TextView> <TextView android:text="YELLOW" android:id="@+id/TextView03" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_weight=".14" android:background="#ffff00" android:gravity="center" android:textColor="#000"></TextView> <TextView android:text="GREEN" android:id="@+id/TextView04" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_weight=".15" android:background="#0f0" android:gravity="center" android:textColor="#000"></TextView> <TextView android:text="BLUE" android:id="@+id/TextView05" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_weight=".14" android:background="#00f" android:gravity="center" android:textColor="#fff"></TextView> <TextView android:text="INDIGO" android:id="@+id/TextView06" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_weight=".14" android:background="#4b0082" android:gravity="center" android:textColor="#fff"></TextView> <TextView android:text="VIOLET" android:id="@+id/TextView07" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_weight=".14" android:background="#ee82ee" android:gravity="center" android:textColor="#000"></TextView> </LinearLayout>
The output is like this
- Aswin Bhim Nath

Comments
Post a Comment